BOILER
EMISSIONS - 1

Combustion
equipment such as boilers generate pollutants such as oxides of sulfur
(with sulfur containing fuels),unburned hydrocarbons,CO and NOx.The latter
two are considered important,particularly in gas fired boilers and gas
turbine plants and regulations are in place indifferent parts of the world
to limit their emissions.Effect of various variables on their formation
is key to understanding some of the measures used to minimize their emissions.
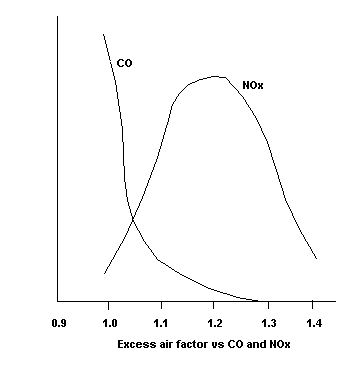
In boilers,excess air is an important factor and its impact on CO and NOx
is shown below.As the excess air increases,CO reduces,while NOx increases
up to a point,above which the combustion temperature is reduced and hence
NOx formation reduces.Large amount of excess air increases the boiler size
and also lowers its efficiency.Hence excess air has to be within a range.Combustion
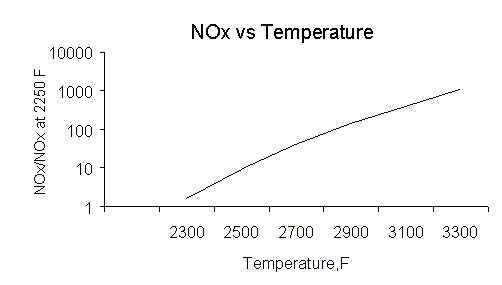
temperature impacts NOx formation significantly;fuels containing hydrogen,which
have a high combustion temperature,for example,generate large amount of
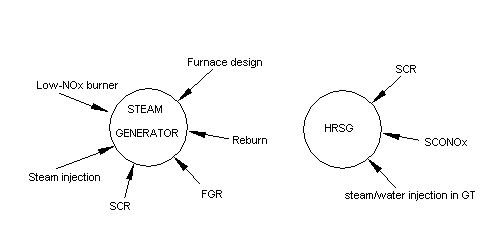
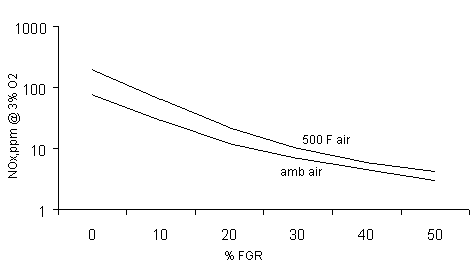
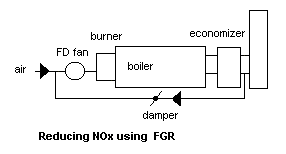
NOx. Flue gas recirculation is a commonly used method to lower NOx in addition
to methods such as steam or water injection and use of low NOx burners.Table
below shows the effect of FGR on combustion temperature.It may be seen
that a large reduction in combustion temperature and hence NOx (on the
order of 50-70 %)can occur with this technique. Staged combustion,in which
air or fuel admission into the burner is staged or admitted downstream
of the initial flame front,is also widely used to lower NOx. When large
reduction in NOx or CO,on the order of 90 % or more is desired,SCR or catalysts
are used.The catalysts speed up the reaction of ammonia with NOx to convert
it to nitrogen and water vapor.CO is converted to CO2.
Package
boilers firing natural gas or fuel oils do not use air heaters as heat
recovery equipment as it increases the combustion temperature,which can
lead to higher NOx. Hence economizers are invariably used as heat recovery
equipment. The use of completely watercooled boiler furnace design(click
here for a picture of completely watercooled furnace design by ABCO)
minimizes
NOx formation by having a cool environment for the flame front,where a
large amount of NOx is formed, while refractory lined front boiler walls
reradiate energy back to the flame,thus increasing the NOx formation.Refractory
lined boilers have other concerns such as maintenance,longer startup periods
and leakage of combustion products from the furnace to outside,resulting
in casing corrosion. The welded partition wall in a completely water cooled
furnace,as compared to skin cased design,also minimizes CO formation by
ensuring a leak proof envelope for the flame and ensures that the hot combustion
products travel to through the entire furnace length before entering the
convection sec tion..Leakage of hot flue gases from the furnace to the
convection section,which is likely in a skin cased design, increases CO
formation and also lowers the boiler efficiency.
Effect of
FGR on combustion temperature
| fuel |
nat gas |
nat gas |
nat gas |
# 2 fuel oil |
# 2 fuel oil |
# 2 fuel oil |
| Excess
air,% |
15 |
15 |
15 |
15 |
15 |
15 |
| FGR,% |
0 |
15 |
30 |
0 |
15 |
30 |
| comb
temp,F |
3227 |
2892 |
2619 |
3354 |
2994 |
2713 |
Techniques
used to lower NOx in boilers and HRSGs

Back to Ganapathy's
Home Page



![]()