 Evaluating
HRSG Field Data
V.Ganapathy
Evaluating
HRSG Field Data
V.Ganapathy

Gas
Turbine HRSGs like other waste heat boilers are designed for a particular
set of conditions but often operate at slightly or even significantly different
gas/steam parameters due to various reasons. The steam pressure could be
different due to plant header conditions;feed water temperature may be
5 to 15 F off due to deaerator operation;more steam could be taken off
the HRSG for deaeration; exhaust gas flow ,temperature and analysis could
be different due to changes in ambient conditions and gas turbine load
and so on..So how does then one reconcile the actual operating data with
the HRSG design data or guarantees?
HRSG
simulation or the HRSGS program could help in determining if the HRSG is
performing as designed even under different gas/steam parameters.This
will be explained using the case of a simple single pressure HRSG.
Example:A
gas turbine HRSG is designed for the parameters shown in Table 1. When
put into operation,the field data was slightly different as shown. The
steam temperature is uncontrolled.
Gas
analysis used :% vol co2=3,h2o=7,n2=75,o2=15.use a heat loss=1% in both
cases.The plant engineer wants to know if the HRSG is doing fine or not
and whether the lower steam generation is solely due to the lower gas flow/inlet
temperature conditions and steam pressure.
Table of design and operating data for HRSG
| condition |
Design/Guarantee |
Operation/test |
| gas
flow,lb/h |
550,000 |
? |
| exhaust
gas temperature,F |
1000 |
970 |
| exit
gas temperature,F |
371 |
380 |
| steam
pressure,psig |
600 |
500 |
| steam
temperature,F |
700 |
690 |
| feed
water temperature,F |
230 |
230 |
| blow
down,% |
2 |
0 |
| steam
flow,lb/h |
79,400 |
68,700 |
The above
situation is not uncommon in cogeneration plants.Let us use HRSGS,the HRSG
simulation program, to see how the HRSG is doing.
(Visit
the HRSG Simulation web site for a Free Demo and information on HRSG simulation)
The
HRSGS program is used to firm up or establish the HRSG 'design'. Using
the gas parameters given in the design case ,the pinch and approach points
are varied till we get the exit gas temperature close to the design value;the
design pinch and approach points are then frozen.The design is also indirectly frozen or established.If the water temperature
at the exit of the economizer is known,the approach point used can also
be verified.The output from the HRSGS program is shown below.
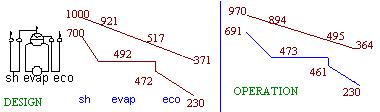 (The
temperatures are in F,gas/steam flows in lb/h and the duty in MM Btu/h
and steam pressure in psia.)
(The
temperatures are in F,gas/steam flows in lb/h and the duty in MM Btu/h
and steam pressure in psia.)
Design Case: Establishing the HRSG Design basis: gas flow=550,000 lb/h
| surface |
gas
in F |
gas
out |
stm
in |
stm
out |
duty |
press |
flow |
%
stm |
pinch |
apprch |
| suph |
1000 |
921 |
492 |
700 |
11.71 |
615 |
79440 |
100 |
|
|
| evap |
921 |
517 |
472 |
492 |
59.36 |
635 |
79440 |
100 |
25 |
20 |
| econ |
517 |
371 |
230 |
472 |
20.77 |
645 |
81029 |
|
|
|
In order
to evaluate the off-design or operating condition,the gas flow is first
determined from the operating data using heat balance methods. Gas flows
are difficult to measure,while gas temperatures,steam/water flows can be
measured more accurately.The energy absorbed by steam is first computed
and using the inlet and exit gas temperatures and the gas analysis,the
gas specific heat or enthalpy is computed from which the gas flow is obtained.
In this case,the gas flow can be shown to be 501,300 lb/h.With this gas flow,the HRSGS program is again run in the off-design
mode and the results are shown below.Note that the steam pressure
is different in the off-design case.
Off-Design
performance:Verifying the operating data: gas flow=501,300 lb/h
| surface |
gas
in F |
gas
out |
stm
in |
stm
out |
duty |
press |
flow |
%
stm |
pinch |
apprch |
| suph |
970 |
894 |
473 |
691 |
10.26 |
515 |
69524 |
100 |
|
|
| evap |
894 |
495 |
461 |
473 |
52.97 |
533 |
69524 |
100 |
22 |
12 |
| econ |
495 |
364 |
230 |
461 |
16.93 |
543 |
69524 |
|
|
|
In order
to arrive at some conclusion,the HRSG supplier and plant owner should agree
to some tolerances in instrument readings,errors in measurements,procedures
used for gathering data etc.The ASME PTC 4.4 gives some information on
these issues.
From
the off-design run,It can be seen that the HRSG should be generating 69,524
lb/h and that the gas exit temperature should be 364 F,while that measured
is higher and the steam flow is also lower.Hence there is reason to
investigate further as even after correcting for the different gas inlet
temperature,flow and steam pressure,the actual performance is off from
that suggested by the simulation process.It is possible that the HRSG
is not adequetely sized or that the steam flow readings,gas temperatures
have to be checked again.In any case,with the HRSGS program,plant engineers
have a tool for evaluating HRSG performance under different parameters
and operating conditions.One cannot simply say that due to differences
in steam pressure or gas flow or temperatures,the HRSG performance is different
from that guaranteed and walk away.HRSGS program also helps the plant engineer
to perform what-if analysis. Using one set of operating data,the performance
at other conditions may be obtained.Say in the future,the feed water temperature
or steam pressure is likely to be different or if the gas turbine is going
to be replaced,the HRSG performance can be easily evaluated using HRSGS
program.One can also see what happens if supplementary firing were to be
done.What is most important is that he can perform these studies himself
without contacting the HRSG supplier or use the HRSG supplied information
to verify his calculations and thus become a knowledgeable customer!
Note that the simulation process
is explained at my web site above and also in my books. One of the major
features,which makes this a simple process is that we don't have to know
the tube/fin configuration,geometry,tube lengths,spacings etc to perform
the above analysis! Hence anyone familiar with heat balances can do it!
[Note that we could have also established the design
using the operating data and then checked the off-design performance using
the guarantee gas inlet conditions and checked for the steam generation].
Note
that this is a simple HRSG configuration.Similar analysis could be
performed for complex,multi-pressure, fired HRSGs. The HRSG supplier and
Plant engineers have to work together and agree to several aspects discussed
above before reaching any drastic conclusions as there are lot of variables
involved.

Books,software,papers
on Boilers,HRSGs,Steam Plant calculations
email Ganapathy
 Evaluating
HRSG Field Data
V.Ganapathy
Evaluating
HRSG Field Data
V.Ganapathy
 (The
temperatures are in F,gas/steam flows in lb/h and the duty in MM Btu/h
and steam pressure in psia.)
(The
temperatures are in F,gas/steam flows in lb/h and the duty in MM Btu/h
and steam pressure in psia.)