
In the manufacture of hydrogen through steam reforming of natural gas or naptha,several waste gas streams are generated.The steam reforming process converts a mixture of hydrocarbons and steam into hydrogen,methane,carbon dioxide,carbon monoxide and water vapor in the presence of a catalyst.The hydrocarbon feed and steam at a pressure of about 30-40 atm enter the primary reformer at about 450 C and a reaction is initiated at 600 C,through combustion of natural gas or naptha. The flue gases thus generated leave the reformer at about 1000 C and energy is recovered from these gases by generating high pressure superheated steam in a flue gas waste heat boiler.This boiler is like a conventional waste heat boiler,consisting of multiple coils and sometimes an air preheater.Sometimes low pressure steam in addition to high pressure steam is also generated.Finned tubes may be used in the cooler gas temperature regions of the boiler as the gas stream is clean. The flue gas pressure is nearly atmospheric.The mixture of feed and steam mixture is often preheated in this waste heat boiler.The high pressure saturated steam generated in the reformed gas boiler is mixed with the saturated steam generated in the flue gas boiler and the total steam is superheated in the flue gas boiler.(it is easier to include superheaters,economizers in the flue gas stream compared to the high pressure reformed gas stream).The steam generated is used to drive steam turbines for auxilliary equipment after generating electricity via a steam turbine.
The tube side effluents from the primary reformer go the secondary reformer before which preheated air is added.Combustion reactions occur and the catalysts convert the methane partly to hydrogen.The effluent called reformed gas and consisting of water vapor,hydrogen,carbon dioxide,carbon monoxide and some methane and nitrogen,enter a waste heat boiler called Reformed gas boiler. Click here to see typical analysis of waste gas streams .Gases are cooled from about 1000 C to 300-350 C.Since the gas pressure is high,fire tube boilers are generally used,though water tube designs are available. Since the exit gas temperature from the boiler is critical for reactions with catalysts downstream,the exit gas temperature is controlled using internal or sometimes external gas bypass system.A few bypass systems are designed such that even in the event of the full opening of the bypass damper,the exit gas temperature is limited to less than 900-1000 F and the downstream equipment are unaffected.Note that the gas temperature leaving the bypass section is typically the inlet gas temperature as there is generally no cooling of the gas in the bypass section.
The heat transfer coefficient with reformed gases is high,on the order of 5 to 7 times that with typical flue gases due to the presence of the hydrogen and water vapor and also the high mass flow rate due to high gas pressure; hence the heat flux on the steam side will be high and is often limited to about 100,000 Btu/ft2h to avoid DNB concerns. Tube sheet design is also given consideration due to this reason. Tube sheets are protected by refractory and ferrules as shown,which are typically made of Inconel 800 or ceramic materials.
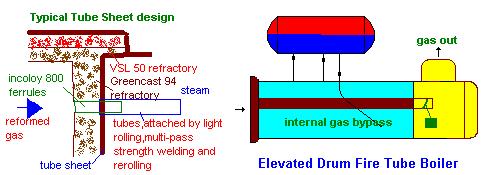
Adequete boiler water circulation is ensured with the help of an elevated steam drum and external downcomers,risers so that the tube sheet and tubes are protected.
Since the gas stream contains hydrogen at high partial pressure,hydrogen embrittlement and corrosion is a consideration in the selection of tube materials. Generally T11 or T22 (chrome-moly) steels are used for boiler tubes. Metal dusting also occurs in carbanaceous atmospheres.It takes the form of pitting,thinning and wastage.The alloy is turned into dust and hence the term.Ensuring that the tube ,tube sheets operate at less than 800 F minimizes this concern.
The cooled gases then enter a shift converter where conversion of carbon moxide to dioxide takes place in the presence of catalysts;hydrogen is also formed. The exothermic reaction raises the gas temperature to about 425 C.The gases are cooled in a converted gas boiler or a series of boilers depending on the % conversion of carbon monoxide.Gas temperature control is important in these boilers,which are similar in design to the reformed gas boiler.The gases then enter a methanator where traces of carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide are converted to methane and water vapor.The methanator outlet gas is cooled in a syn gas exchanger and condensate is removed.The gas is then compressed to very high pressure,about 250-350 atm,and enters a converter where nitrogen and hydogen interact to form ammonia,which is a component of fertilizers.
The scheme shown above may have several variations depending on the engineering of the system.From heat recovery viewpoint,the flue gas and reformed gas boilers are significant.In small hydrogen plants,the flue gas boiler and reformed gas boilers may be built into a single package with a common steam drum;see the author's book on waste heat boilers.