HRSG
EFFICIENCY AND SUPPLEMENTARY FIRING
This
article briefly explains the meaning of HRSG efficiency and why fired gas
turbine HRSGs are more efficient than unfired HRSGs.
Per
ASME Power Test Code 4.4,the HRSG efficiency is defined as:
E=(energy
to steam/water/fluids)/[exhaust gas flowxenthalpy+fuel input on LHV basis]
Compared
to an unfired HRSG,the fired unit is more efficient for the following reasons:
 Addition
of auxilliary fuel reduces the effective excess air in the exhaust gases,as
no air is added. The fuel utilizes only the excess oxygen in the turbine
exhaust. This is opposite to what happens in a steam generator,where with
increase in excess air,the heat losses are more and thus efficiency is
reduced.
Addition
of auxilliary fuel reduces the effective excess air in the exhaust gases,as
no air is added. The fuel utilizes only the excess oxygen in the turbine
exhaust. This is opposite to what happens in a steam generator,where with
increase in excess air,the heat losses are more and thus efficiency is
reduced.
 With
increased steam generation,usually the exhaust gas temperature decreases in
a single pressure system. This is due to the increased ratio of steam/gas. In
a conventional steam generator,the gas/steam ratio is nearly constant,while in a HRSG,the exhaust gas flow remains the same,while the steam generation
increases due to auxilliary firing. The increased water flow through the
economizer(with gas flow remaining same) can pull the gas temperature further
down due to the increased duty.
With
increased steam generation,usually the exhaust gas temperature decreases in
a single pressure system. This is due to the increased ratio of steam/gas. In
a conventional steam generator,the gas/steam ratio is nearly constant,while in a HRSG,the exhaust gas flow remains the same,while the steam generation
increases due to auxilliary firing. The increased water flow through the
economizer(with gas flow remaining same) can pull the gas temperature further
down due to the increased duty.
The
following table shows the performance of a saturated steam HRSG at different
loads.The data were generated using the HRSGS simulation program described
elsewhere.HRSG Simulation
Effect of auxilliary firing on HRSG efficiency
| item |
case 1 |
case 2 |
case3 |
| gas flow,lb/h |
150,000 |
150,000 |
150,000 |
| inlet gas temp,F |
900 |
900 |
900 |
| firing temp,F |
900 |
1290 |
1715 |
| fuel,MM Btu/h(L) |
0 |
17.3 |
37.6 |
| steam flow,lb/h |
22,780 |
40,000 |
60,000 |
| steam press,psig |
200 |
200 |
200 |
| feed water in,F |
240 |
240 |
240 |
| exit gas temp,F |
327 |
315 |
310 |
| duty,MM Btu/h |
22.67 |
39.9 |
59.9 |
| efficiency,% |
68.7 |
79.2 |
84.9 |
Note
that duty refers to energy absorbed by steam.
Exhaust
gas analysis=% vol CO2=3,H2O=7,N2=75,O2=15.
blow
down=3%. fuel input is on LHV basis.
It
may be seen that the exit gas temperature decreases as steam generation
increases. Also,the additional fuel input is nearly equal to the additional
duty.In case 2,the fuel input=17.3 MM Btu/h ,while the additional steam
duty=17.3 MM Btu/h.
This
means that the fuel to steam efficiency is 100 %. In a conventional steam
generator this efficiency is only about 92-93 % on LHV basis. Engineers
have to understand this important difference between HRSGS and steam generators.This
concept can be used to generate steam efficiently in cogeneration plants.
GENERATING
STEAM EFFICIENTLY IN COGENERATION PLANTS
In
order to generate steam efficiently in plants which have both gas turbine
HRSGs and packaged boilers,one should first understand the load versus
performance curves for both types of boilers.
STEAM
GENERATOR CHARACTERISTICS
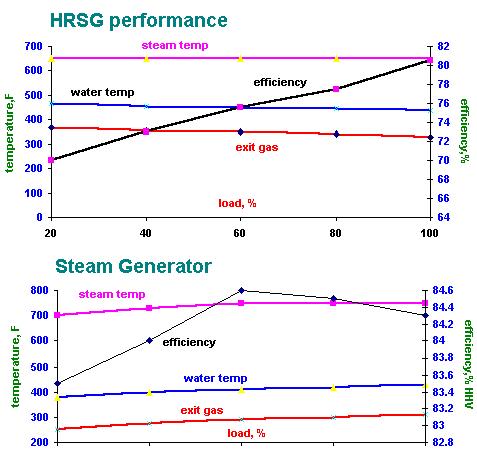
It
can be seen from the figure that:
 Exit
gas temperature increases with load. This is due to the increased flue
gas flow through the boiler with load.
Exit
gas temperature increases with load. This is due to the increased flue
gas flow through the boiler with load.
 Efficiency
increases and then falls off slightly. This is due to the combination of
flue gas heat losses and casing losses. The casing loss remains constant
in Btu/h(for a given ambient condition).However as a % of load,it decreases
with load.If the casing loss is say 1 % at 100 % load,it will be 4 % at
25 % load.The flue gas losses (see ASME PTC 4.1) increase with load due
to the higher exit gas temperature. The combination of these losses thus
results in a parabolic shape for the efficiency curve. The efficiency peaks
in the range of 60-70 % load typically.
Efficiency
increases and then falls off slightly. This is due to the combination of
flue gas heat losses and casing losses. The casing loss remains constant
in Btu/h(for a given ambient condition).However as a % of load,it decreases
with load.If the casing loss is say 1 % at 100 % load,it will be 4 % at
25 % load.The flue gas losses (see ASME PTC 4.1) increase with load due
to the higher exit gas temperature. The combination of these losses thus
results in a parabolic shape for the efficiency curve. The efficiency peaks
in the range of 60-70 % load typically.
 Also
note that the difference in efficiency between say 25 and 100 % loads is
small,about 1.5 %.
Also
note that the difference in efficiency between say 25 and 100 % loads is
small,about 1.5 %.
HRSG
CHARACTERISTICS
 As
seen earlier,the efficiency increases with load significantly.
As
seen earlier,the efficiency increases with load significantly.
 The
exit gas temperature decreases as load increases due to reasons given earlier.
The
exit gas temperature decreases as load increases due to reasons given earlier.
Using these characteristics,the plant engineer can compute the fuel consumption
at various loads for each type of boiler and load each in such a way that the total fuel consumption is minimized to the extent possible.Maximizing
the HRSG steam output first will help minimize the total fuel consumption.
A
curve showing steam output versus fuel consumption may be developed for different combinations of the HRSG and steam generators.
This will give an idea of how to load or use the various boilers.
.
 Books,Software
on Boilers,HRSGS by V.Ganapathy
Books,Software
on Boilers,HRSGS by V.Ganapathy
 email
Ganapathy
email
Ganapathy
 Addition
of auxilliary fuel reduces the effective excess air in the exhaust gases,as
no air is added. The fuel utilizes only the excess oxygen in the turbine
exhaust. This is opposite to what happens in a steam generator,where with
increase in excess air,the heat losses are more and thus efficiency is
reduced.
Addition
of auxilliary fuel reduces the effective excess air in the exhaust gases,as
no air is added. The fuel utilizes only the excess oxygen in the turbine
exhaust. This is opposite to what happens in a steam generator,where with
increase in excess air,the heat losses are more and thus efficiency is
reduced.
 Generating Steam Efficiently in Cogeneration Plants
by V.Ganapathy
Generating Steam Efficiently in Cogeneration Plants
by V.Ganapathy

