Cheng
Cycle Heat Recovery System
V.Ganapathy

For
plants requiring power and process steam,a simple cycle consisting of a
gas turbine and HRSG is adequete when the thermal load or process steam
demand is constant.However when the process steam demand drops off,the
exhaust gas may have to be bypassed,which is a waste of energy or the gas
turbine load may have to be decreased,which is also not a good solution.
An extraction steam turbine added to the system can help handle process
steam variations;however the resulting combined cycle is expensive and
has more components for a small plant.The Cheng cycle is a good solution
to these type of situations.
The
Cheng cycle,see figure below,helps plants generate varying amounts of electrical
power and process steam depending upon the demand of each without having
to compromise on either.It offers a few advantages over combined cycle
plants.
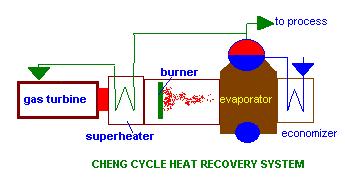
The
Cheng cycle consists of a gas turbine,which is capable of being injected
with large amount of superheated steam(15 to 20 % of the exhaust flow)
and a HRSG which can generate both saturated as well as superheated steam
with firing capability.The ratio between amount of superheated and saturated
steam can be varied by using control valves in the line to the superheater
and at the process steam outlet.Electrical power increases as more of
high temperature superheated steam is injected into the gas turbine and
vice versa(due to the increased gas mass flow and higher specific heat).Process
steam needs can be handled by decreasing the amount of superheated steam
generated. Hence we are able to achieve a wide ranging electrical and process
steam demand variations using this concept,which is also simpler with fewer
compnents compared to a combined cycle.Note that the duct burner is located
between the superheater and the evaporator.This enables the superheater
to run dry at times as discussed below.
There
are basically 4 modes of operation with widely varying combinations within
these boundary points.
 Unfired mode with all superheated steam injected into the gas turbine;
maximum electrical power is generated,nearly 50 to 70% more than that without
injection.No process steam is provided.The gas analysis to the HRSG will
have to consider the large amount of steam injected. Large % volume of
water vapor and mass flow increases the gas specific heat and thermal
conductivity and hence heat transfer ability,heat flux,gas pressure drop
etc.
Unfired mode with all superheated steam injected into the gas turbine;
maximum electrical power is generated,nearly 50 to 70% more than that without
injection.No process steam is provided.The gas analysis to the HRSG will
have to consider the large amount of steam injected. Large % volume of
water vapor and mass flow increases the gas specific heat and thermal
conductivity and hence heat transfer ability,heat flux,gas pressure drop
etc.
 Unfired mode with no injection of superheated steam. Only saturated steam
for process is generated in this mode.The superheater runs dry.Normal
electrical power is generated by the gas turbine.
Unfired mode with no injection of superheated steam. Only saturated steam
for process is generated in this mode.The superheater runs dry.Normal
electrical power is generated by the gas turbine.
 Full injection of steam with full firing of the duct burner.Maximum electrical
power is generated with significant amount of process steam.Both superheated
and saturated steam are generated.
Full injection of steam with full firing of the duct burner.Maximum electrical
power is generated with significant amount of process steam.Both superheated
and saturated steam are generated.
 Fully fired with no steam injection. Maximum process steam is generated.
Superheater runs dry.
Fully fired with no steam injection. Maximum process steam is generated.
Superheater runs dry.
As
mentioned earlier,one can vary the amount of injection steam or amount
of firing to have several operating points within these 4 major boundary
points.
With
a modified Allison 501 KB gas turbine,the electrical power output varies
from about 3.5 to 5.5 MW,while process steam can vary from nil to 50,000
lb/h at about 200-400 psig.
The
following points should be noted with respect to the design of the HRSG.
The
superheater can run dry and wet on and off,depending upon the power and
process steam demand and electrical/thermal load scheduling.(Some plants
use the Cheng cycle to maximize on the sale of power when electricity
costs are expensive and optimize on a ratio between electrical power,process
steam based on cost of electricity and process steam.) Hence there is a
possibility of exfoliation (dislodging and carrying away with steam) of
iron oxide deposits from the inside of superheater tubes into the gas turbine.
This concern is minimized by using alonized T11 tubes.Chromizing may also
be considered,however this may be more expensive.
The
turbine exhaust gas contains nearly 30% water vapor and 11 % oxygen (versus
7 % water vapor,14 % oxygen in dry mode) when full injection occurs.Hence
in order to ensure stability of the duct burner flame,an augmenting air
fan is added to the burner system.
NOx
is reduced due to the injection of steam in the gas turbine,which is an
additional advantage of the system.
In
order to ensure excellent steam purity of steam for injection into the
gas turbine(less than 10 ppb sodium),an external steam separator is added
in the line between the drum and superheater.
In
order to improve the efficiency of the system and reduce the amount of
deaeration steam,a feed water preheater is included. This exchanger preheats
the makeup water going into the deaerator,while cooling the feed water
to the economizer.
More
information is available in the author's Waste Heat Boiler Deskbook.

V.Ganapathy's
Homepage(Books,Articles,Software on Boilers,HRSGs)
email Ganapathy